In this post, we’ll discuss the difference between absolute threshold vs difference threshold and how it relates to psychology.
Before we discuss absolute threshold vs difference threshold, let’s back up and discuss sensory thresholds. Sensory threshold is defined as the level a stimulus must reach to be detected by a human’s senses. There are different sensory thresholds defined in psychology, including; absolute threshold, difference threshold, differential threshold, recognition threshold, and terminal threshold. Let’s begin with their basic definitions:
- Absolute threshold is the lowest level of magnitude or strength a stimulus needs to reach for sensory systems to be activated.
- Difference threshold is the minimum level of stimuli that someone can detect 50% of the time.
- Recognition threshold is the level at which a detected stimulus can be recognized and distinguished.
- Differential threshold is the level at which an increase of a stimulus can be detected.
- Terminal threshold is the level at which an increase of stimulus in intensity no longer increases its perception.
Absolute Threshold vs Difference Threshold
Absolute threshold is the minimum level at which stimuli can be detected. For example, when a sound is just loud enough to be detected, but not loud enough so that it is obviously detectable or recognizable, the perception of that sound is occurring at the absolute threshold. In contrast, difference threshold is the level of stimulus required for someone to detect the stimulus 50% of the time.
Absolute Threshold Experiments
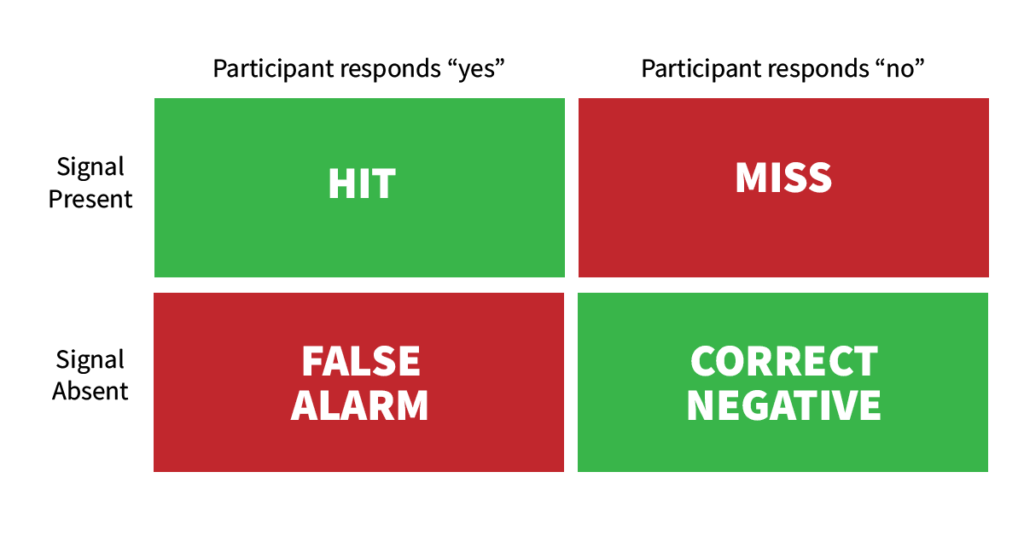
Experiments used to determine the absolute threshold in perception include the following trials:
- Catch Trials: a signal detection test where a stimulus is presented and a subject is asked to confirm if the stimulus was presented
- Hit: when someone correctly confirms that stimulus was presented
- Miss: when someone fails to confirm that stimulus was presented
- Noise Trials: a signal detection test where a stimulus is not presented and a subject is asked to confirm if a stimulus was presented.
- False alarms: when someone incorrectly confirms that a stimulus was presented
- Correct negative: when someone correctly confirms that stimulus was not presentedResponse bias is detected when a subject presents a significant number of misses or false alarms.
Threshold of conscious perception are commonly referred to as limina. Subliminal perception is an aspect of perception often called “perception without awareness.” It refers to the perception of stimuli presented below a given threshold. Stimuli below the absolute threshold are not transduced. Therefore, they never reach the central nervous system. However, some information below the threshold of conscious perception will still arrive to the CNS. However, they will not reach the higher-order brain circuits and regions controlling consciousness and attention.
Discrimination Testing Difference Threshold
Discrimination Testing (psychophysical discrimination testing) is a testing method to determine if two stimuli are perceptibly different. The formal definition employed in psychological testing explains that the difference threshold is the minimum level of stimuli that someone can detect 50% of the time. During a discrimination testing procedure, the participant is presented with a set of stimuli that vary slightly from each other and then the participant is asked to determine whether there is a difference. The stimuli is continuously presented until the participant is able to determine a change. Difference thresholds apply to all perception senses: hearing, smell, taste, touch, vision, and touch. Instead of being measured as a whole number, difference thresholds are also regarded as percentage of change.
Weber’s Law
Weber’s law is a psychological law that quantifies the noticeable change in a stimulus (a ratio of the original stimulus). As the magnitude of stimuli increases, the difference threshold must also increase.
Signal detection theory
Signal detection theory states that stimuli perception can be affected by physical and psychological factors (or non-sensory factors) such as motives, memory, expectations. This theory emphasizes how internal and external (psychological and environmental) contexts may influence our perception of the same stimuli. Signal detection theory allows for the explanation of the response bias phenomenon: the tendency of people to systematically respond to a stimulus in a particular way with the influence of external factors. For example, some people may answer questionnaires based on socially acceptable answers instead of their true opinions. This typically occurs in instances where subjects are asked to self-report information or experiences.
Sensory adaptation
Sensory Adaptation is a phenomenon that occurs when our senses stop perceiving a continuous stimulus. It may have physiological (sensory) and/or psychological (perceptual) components. For example, to acclimate to darkness, pupils may dilate in the dark. To acclimate loud noises, the ear muscles will reduce ear vibrations by contracting. This is also applicable to somatosensory stimuli, as cold water may begin to feel less cold over time. Sensory adaptation works as a process for the body to direct its attention to relevant stimuli. If stimuli is constantly present, the body and nervous system will focus its resources on identifying new stimuli.
Psychophysics
Psychophysics is the psychological study of the interplay between the physical nature of different stimuli and the sensations, perceptions, and mental processes they evoke. Tests rely on threshold measurements, signal detection theory, and ideal observer analysis. Methods for these tests include method of limits, constant stimuli, and adjustment.
Resources: